
Os campi universitários modernos exigem uma infraestrutura de rede de alta velocidade, confiável e escalável. As soluções de modo único MPO representam a escolha ideal para a interconexão de campus over longas distâncias. Essas soluções oferecem alta largura de banda e simplificam a implantação de redes. Robusto MPO Trunk Cable Forma o núcleo desses sistemas. Um Adaptador de MPO facilita conexões contínuas e sem interrupções. Esta tecnologia garante, de forma eficaz, que as redes estejam preparadas para atender às demandas crescentes de dados no futuro. Os sistemas MPO de longo alcance apoiam a inovação e o crescimento em ambientes acadêmicos.
Key Takeaways
- A fibra ótica de modo único MPO ajuda a conectar edifícios dentro de um campus über longas distâncias. Ele oferece uma conexão à Internet rápida e confiável.
- Esta tecnologia oferece uma velocidade de internet extremamente alta. É capaz de lidar com isso Conexões de 100G, 400G e até mais rápidas.
- Cabos MPO de modo único Funciona bem para distâncias muito longas. Eles conectam edifícios que estão distantes um do outro sem que haja perda de sinal.
- Estes cabos são fáceis de instalar. Eles vêm prontos para serem conectados, o que economiza tempo e dinheiro.
- As soluções de modo único MPO economizam espaço. Eles utilizam menos cabos, o que torna as áreas de rede mais arrumadas e organizadas.
- Este sistema está preparado para o futuro. É capaz de crescer facilmente e se adaptar às novas tecnologias conforme necessário.
- Manter os conectores MPO limpos é muito importante. A sujeira pode causar problemas na rede e diminuir a velocidade da internet.
O cenário em constante evolução da conectividade nos campi universitários exige atenção especial
As instituições educacionais modernas enfrentam uma pressão crescente para fornecer conectividade de rede robusta e de alta velocidade. Atualmente, os campi universitários dependem em grande medida de recursos digitais para o ensino, a pesquisa e as operações diárias. Essa dependência impõe a necessidade de infraestrutura de rede avançada.
Limitações dos Cabos Tradicionais para Ligações em Campi Extensos
Os métodos tradicionais de cabeamento frequentemente têm dificuldades em atender às exigências de ambientes universitários extensos. Elas representam obstáculos significativos para a interconexão a longa distância.
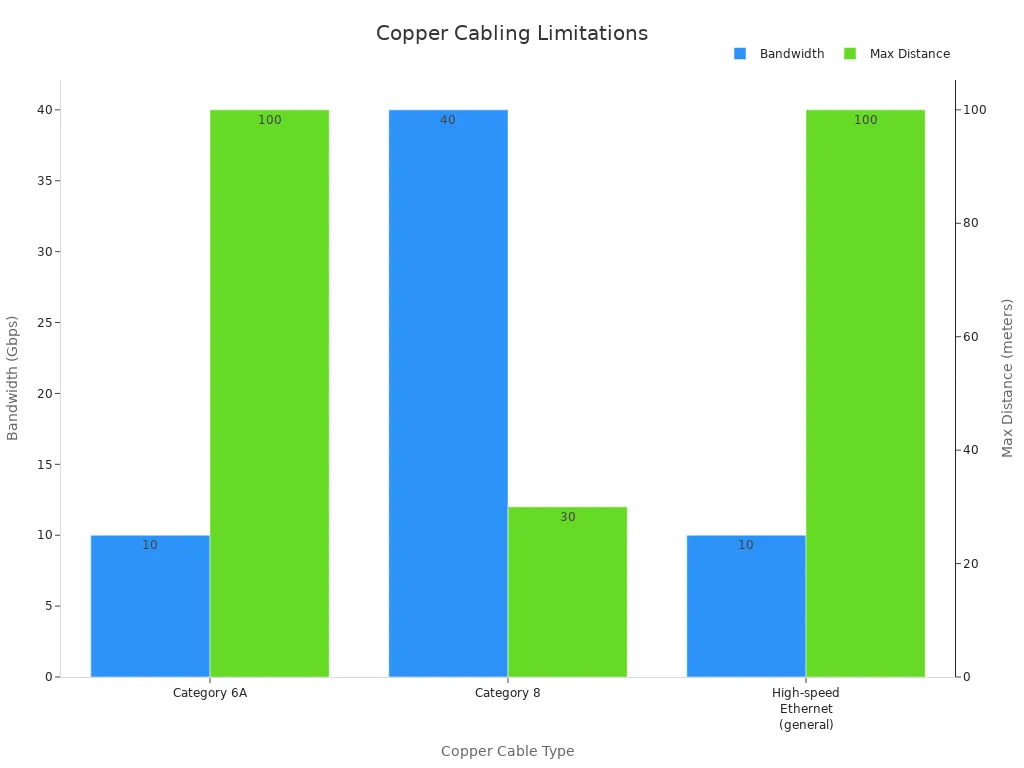
Cabo de Cobre: Restrições de Distância e Largura de Banda
O cabeamento de cobre, uma solução consagrada há muito tempo, apresenta limitações inerentes quando utilizado em distâncias extensas. A degradação do sinal, conhecida como atenuação, restringe seu alcance efetivo. Conexões Ethernet de alta velocidade, como as de 1 Gbps ou 10 Gbps, normalmente operam dentro de um alcance efetivo máximo de 100 metros. Além dessa distância, o sinal enfraquece consideravelmente. Isso exige a utilização de repetidores ou amplificadores para manter a integridade do sinal.
| Tipo de Cabo de Cobre | Largura de banda | Distância Máxima |
|---|---|---|
| Categoria 6A | 10 Gbps | 100 metros |
| Categoria 8 | 25–40 Gbps | 30 metros |
| Ethernet de alta velocidade (geral) | 1 Gbps ou 10 Gbps | 100 metros |
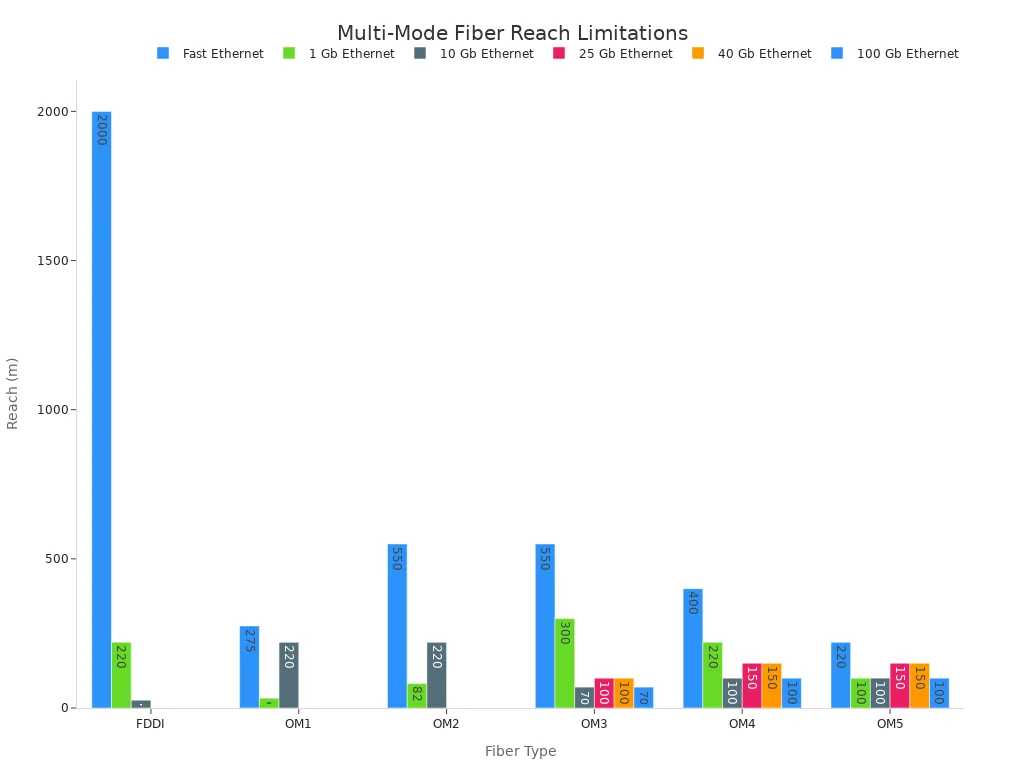
Fibra Multimodo: Dispersão Modal e Limitações de Alcance
A fibra ótica de múltiplos modos é adequada para distâncias mais curtas, como dentro de edifícios individuais. Seu grande diâmetro do núcleo permite que vários modos de luz se propaguem. Isso leva a… dispersão modalO que limita o comprimento máximo de uma ligação de transmissão. Diferentes velocidades dos vários modos de luz fazem com que o pulso luminoso se espalhe ao longo da distância, introduzindo interferências entre os símbolos transmitidos. Comprimentos de transmissão mais longos resultam em uma maior dispersão modal. A dispersão cromática, causada pelas fontes de luz LED que produzem uma gama de comprimentos de onda, limita ainda mais o comprimento útil dos cabos de fibra ótica de múltiplos modos.
| Tipo de fibra | Fast Ethernet 100BASE-FX | 1 Gb Ethernet 1000BASE-SX | 10 Gb Ethernet 10GBASE-SR | Eternet de 25 GB, 25GBASE-SR | Ethernet de 40 GB, 40GBASE-SR4 | Ethernet de 100 Gb, 100GBASE-SR10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FDDI (62,5/125) | 2000 m | 220 m | 26 m | Não compatível | Não compatível | Não compatível |
| OM1 (62,5/125) | 275 m | 33 m | 220 m | Não compatível | Não compatível | Não compatível |
| OM2 (50/125) | 550 m | 82 metros | 220 m | Não compatível | Não compatível | Não compatível |
| OM3 (50/125) | 550 m | 300 m | 70 m | 100 m | 100 m | 70 m |
| OM4 (50/125) | 400 m | >220 m | 100 m | 150 m | 150 m | 100 m |
| OM5 (50/125) | >220 m | 100 m | 100 m | 150 m | 150 m | 100 m |
O imperativo de uma infraestrutura de alta capacidade e preparada para o futuro
Os campi universitários necessitam de uma infraestrutura de rede que suporte as necessidades atuais e se adapte aos futuros avanços tecnológicos. Isso exige soluções de alta capacidade e preparadas para o futuro.
Suporte a Aplicações Acadêmicas e de Pesquisa Intensivas em Termos de Utilização de Dados
As aplicações acadêmicas e de pesquisa modernas geram e processam grandes volumes de dados. Os laboratórios de pesquisa frequentemente lidam com grandes conjuntos de dados e imagens detalhadasIsso exige capacidades de rede robustas.
- Os laboratórios de pesquisa frequentemente lidam com grandes conjuntos de dados e imagens detalhadas.
- O aprendizado e a pesquisa modernos exigem uma conexão Wi-Fi confiável e de alto desempenho para suportar sistemas de áudio e vídeo, dispositivos da Internet das Coisas e numerosos usuários conectados.
- Todos os sistemas que se conectam à rede de pesquisa devem fazê-lo através do ponto especificado 10 gigabits.
- Uma arquitetura de rede projetada especificamente para aplicações de alto desempenho distingue o uso em pesquisas do uso para fins gerais.
Viabilização de Iniciativas de Campus Inteligente e Integração com a Internet das Coisas
O aumento das iniciativas de campus inteligentes e a integração de dispositivos da Internet das Coisas sobrecarregam ainda mais as redes existentes. Essas tecnologias exigem uma conectividade abrangente e confiável. Os campi universitários utilizam sensores, iluminação inteligente e sistemas de gestão inteligente de edifícios. Esses sistemas geram fluxos contínuos de dados.
Assegurar a confiabilidade da rede para operações críticas
A confiabilidade da rede continua a ser de suma importância para as operações críticas do campus. Isso inclui funções administrativas, serviços de emergência e sistemas de segurança. Qualquer interrupção no funcionamento da rede pode afetar seriamente a segurança e a produtividade do campus. Uma estrutura de rede confiável garante a operação contínua de todos os serviços essenciais.
Compreender a tecnologia de modo único MPO para conexões de longa distância com este tipo de tecnologia

Os campi universitários precisam de soluções de rede avançadas. A tecnologia de modo único MPO oferece uma combinação poderosa para conexões de longa distância. Esta seção explora os componentes e os benefícios dessa abordagem.
O que é a tecnologia MPO (Multi-fiber Push On)?
MPO Technology Fornece conectividade de fibra ótica de alta densidade. Isso agrega várias fibras ópticas em uma única interfaceEste design economiza espaço e melhora a eficiência em ambientes de alta densidade.
Conectores de Multifibra de Alta Densidade
Os conectores MPO são conectores de fibra ótica que incorporam várias fibras ópticas. Eles possuem um arranjo linear de fibras dentro de uma única ferrula. Esses conectores geralmente vêm acompanhados de… 8, 12, 16 ou 24 fibrasSão utilizados principalmente em data centers para consolidar várias fibras em cabos de backbone. Os conectores MPO também suportam aplicações ópticas em paralelo. Essas aplicações transmitem e recebem sinais através de múltiplas fibras para alcançar velocidades mais elevadas.
Conexão e Desconexão Simplificadas
Os conectores MPO oferecem um mecanismo de conexão tipo “push-on”. Isso permite uma conexão e desconexão rápidas e fáceis. Os técnicos podem conectar muitas fibras simultaneamente. Isso reduz significativamente o tempo de instalação em comparação com conexões de fibra ótica individuais. O processo simplificado também minimiza o potencial de erros humanos durante a implementação.
As Vantagens da Fibra de Modo Único para Distâncias Longas
A fibra de modo único é essencial para ligações de rede de longo alcance. Oferece desempenho superior em distâncias longas.
Atenuação Ultra-Baixa e Alcance Ampliado
As fibras de modo único oferecem… Principais vantagens táticas para uma conectividade de alta largura de banda e baixa atenuaçãoSeu núcleo estreito permite que um único modo de luz seja transmitido por dezenas de quilômetros. Isso acontece sem a necessidade de amplificadores de sinal ou repetidores. A fibra de modo único possui um diâmetro do núcleo significativamente menor8 a 10 micrómetros) em comparação com a fibra multimodo. Isso reduz a perda de sinal e permite comunicações over longas distâncias. É capaz de transmitir dados a distâncias muito maiores, geralmente até 100 km, sem a necessidade de regeneração do sinal. Isso excede em muito as capacidades da fibra multimodo.
Capacidade de largura de banda inigualável para o crescimento futuro
A fibra de modo único suporta uma largura de banda sem precedentes. Ele lida com grandes volumes de dados para aplicações como redes 5G e transmissão de vídeo em alta definição. Oferece uma largura de banda elevada, o que a torna ideal para atividades que exigem grande uso da rede. Isso inclui o streaming e a transferência de arquivos grandes, devido à baixa atenuação do sinal. Também se destaca na transmissão de dados over longas distâncias, alcançando distâncias consideráveis 140 quilômetros sem amplificação do sinalSuporta taxas de transferência de dados de até 100 gigabits por segundo (Gbps) e mais.
A Sinergia entre MPO e Modo Único para as Estruturas de Base dos Campi Universitários
A combinação de fibras MPO e fibras monomodais cria uma solução poderosa para redes campus. Essa sinergia atende tanto aos requisitos de densidade quanto aos de distância.
Combinar alta densidade com desempenho em longas distâncias
Os conectores MPO fornecem a alta densidade de fibras necessária em espaços compactos. A fibra de modo único oferece alcance e largura de banda ampliados, essenciais para conexões em todo o campus. Esta combinação garante o uso eficiente do espaço disponível para cabos e uma transmissão de dados confiável entre edifícios. Isso o torna ideal para… MPO de longo alcance Estruturas fundamentais do campus.
Implantação simplificada com soluções pré-finalizadas
As soluções de modo único MPO geralmente são fornecidas em forma de conjuntos pré-terminados. Esses cabos chegam da fábrica com os conectores já instalados. Esta abordagem de tipo “conecte e use” simplifica bastante a instalação. Reduz a necessidade de emendas no local e de ferramentas especializadas. Isso economiza tempo e reduz os custos de mão de obra durante a implementação da rede.
Principais Vantagens do Modo Único MPO para Interconexões em Campi Universitários
As soluções de modo único MPO oferecem vantagens significativas para a conexão de edifícios em um campus universitário. Estes benefícios atendem às crescentes demandas dos ambientes educacionais modernos. Eles fornecem uma estrutura de rede robusta e eficiente.
Suporte sem precedentes para largura de banda e taxa de transferência de dados
A fibra ótica de modo único MPO oferece capacidades excepcionais em termos de largura de banda. Isso permite suportar as aplicações de rede mais exigentes. Isso garante que os campi universitários sejam capazes de lidar com o tráfego de dados atual e futuro.
Ativar suporte para velocidades de 100G, 400G e superiores em redes principais
A tecnologia de modo único MPO fornece a infraestrutura necessária para redes centrais de alta velocidade. Suporta facilmente taxas de transferência de dados de 100 Gigabits Ethernet (100G), 400 Gigabits Ethernet (400G) e até maiores ainda. Essa capacidade permite uma transferência rápida de dados entre os prédios do campus. Também facilita o funcionamento eficiente de programas acadêmicos e de pesquisa que requerem grande volume de dados. Os campi podem utilizar servidores e sistemas de armazenamento potentes com total confiança.
Preparação para o futuro com os padrões de Ethernet de próxima geração
Investir em soluções de modo único da MPO prepara os campi universitários para futuros avanços tecnológicos. Este tipo de fibra oferece uma capacidade imensa. Ele se adapta facilmente aos novos padrões de Ethernet que vêm surgindo. Isso garante que a rede permaneça relevante e eficiente por muitos anos. Os campi universitários evitam reformas infraestruturais dispendiosas e perturbadoras. Eles mantêm uma vantagem competitiva no aprendizado e na pesquisa digitais.
Capacidades de Alcance e Distância Ampliados
A fibra de modo único se destaca na transmissão de dados over longas distâncias. Isso o torna ideal para ambientes de campi universitários extensos. Supera efetivamente as barreiras geográficas.
Conectando Edifícios Dispersos Sem Amplificação de Sinal
Campus grandes geralmente possuem edifícios espalhados por distâncias consideráveis. A fibra ótica de modo único MPO conecta de forma eficiente essas estruturas dispersas. Ela transmite dados por distâncias de dezenas de quilômetros sem a necessidade de amplificadores de sinal ou repetidores. Isso reduz a complexidade e os custos de manutenção. Isso também garante um desempenho de rede consistente em todo o campus.
Superando Desafios Geográficos em Campi Universitários Extensos
Características geográficas como rios, estradas ou terrenos irregulares podem complicar a implantação de redes. As soluções de modo único MPO oferecem uma maneira confiável de superar esses obstáculos. Sua capacidade de comunicação over longa distância minimiza a necessidade de equipamentos de rede intermediários. Isso simplifica o planejamento e a instalação. Garante uma conexão contínua, independentemente da disposição do campus.
Instalação simplificada e redução do tempo de implementação
As soluções em modo único da MPO simplificam o processo de instalação da rede. Eles oferecem uma significativa economia de tempo e custos. Isso beneficia os departamentos de TI dos campi universitários.
Conjuntos MPO pré-terminados, tipo “plug-and-play”
Os conjuntos MPO pré-terminados chegam prontos para uso imediato. Os fabricantes instalam os conectores em um ambiente de fábrica controlado. Este design “plug-and-play” elimina a necessidade de procedimentos complexos de terminação de fibras no local. Os técnicos simplesmente conectam os cabos. Isso acelera significativamente o processo de implementação. Também reduz o potencial de erros na instalação.
Minimizar os custos de emenda no local e os custos trabalhistas
A instalação tradicional de fibras geralmente requer muitos trabalhos de emenda no local. Este processo é demorado e exige competências especializadas, bem como equipamentos específicos. Os conjuntos MPO pré-terminados eliminam em grande parte essa necessidade. Isso reduz o tempo de instalação até 80% quando comparado com as terminações de campo. A terminação dos cabos costuma ser a parte mais demorada e que requer mais esforço na instalação de cabos. Essa eficiência se traduz diretamente em menores custos com mão de obra. Os campi universitários podem esperar reduções nos custos de mão de obra de até 50% ou mais.
| Metric | Faixa de Redução (MPO Pré-Terminado vs. Tradicional) |
|---|---|
| Tempo de instalação | De 40% a 80% (ou até mesmo 10% no tempo tradicional) |
| Custos de mão de obra | Até 50% ou mais |
Esta tabela destaca as economias substanciais que podem ser obtidas Isso é alcançado através de soluções MPO com terminação prévia. Eles oferecem uma estratégia de implementação econômica e eficiente.
Eficiência Espacial e Gestão Otimizada de Cabos
As redes de campus modernas operam em ambientes onde o espaço físico costuma ser um recurso escasso e valioso. O uso eficiente do espaço e a gestão organizada dos cabos são cruciais para o desempenho e a manutenção da rede. As soluções em modo único da MPO oferecem vantagens significativas nestas áreas.
Conectores MPO Compactos para Ambientes de Alta Densidade
Os conectores MPO aumentam significativamente a eficiência no uso do espaço e a organização dos cabosEles permitem que um único cabo transporte várias fibras. Isso reduz a dimensão física da rede. Essa consolidação simplifica tanto a instalação quanto a manutenção contínua. Menos cabos significam que é necessário gerenciá-los menos. Em ambientes de alta densidade, os conectores MPO simplificam significativamente a gestão dos cabos. Eles reduzem o número de cabos individuais necessários. Isso resulta em menos desordem e em um risco menor de erros. Os cabos tronco MPO são indispensáveis para aumentar a densidade das redes de fibra óticaIsso é especialmente verdadeiro em data centers, onde o espaço e a eficiência são fatores críticos. Eles permitem a construção rápida de infraestruturas essenciais. Eles reduzem inúmeros enlaces de fibra a um tamanho físico mínimo. Um único cabo contém várias fibras. Isso simplifica a interface de conexões de rede. Este design permite uma conectividade de alta densidade, uma melhor organização dos sistemas de cabos troncos de fibra MPO e um melhor gerenciamento desses sistemas. O resultado é menos congestionamento e uma manutenção mais eficiente na área de trabalho. Os conectores MTP®/MPO contribuem para a economia de espaço, pois… Consolidar 12, 24 ou até mesmo 32 fibras dentro de uma única interface. Isso aumenta drasticamente a densidade dos portos. Isso permite que os data centers acomodem um número significativamente maior de conexões no mesmo espaço físico, dentro de um rack. Para uma gestão otimizada dos cabos, esta tecnologia integra várias fibras em um único conjunto de cabo robusto. Isso reduz drasticamente o número total de cabos necessários. Isso libera espaço essencial em canais e bandejas de cabos. Por exemplo, um cabo tronco MTP®/MPO-12 personalizado pela KEXINT pode suportar até 144 ou 288 fibras em apenas uma distância de instalação. Isso efetivamente substitui dezenas de cabos de conexão tipo duplex. Melhora a circulação do ar, facilita a organização dos itens e reduz os erros de conexão.
Redução do volume dos cabos em conduites e racks
A natureza compacta dos cabos de modo único MPO resolve diretamente o problema do grande volume dos cabos. Os métodos tradicionais de cabeamento geralmente resultam em canais e prateleiras superlotados. Isso pode impedir a circulação do ar e complicar a resolução de problemas. As soluções MPO consolidam muitos fios de fibra individuais em um único cabo revestido. Isso reduz significativamente o volume total de cabos necessários. Isso cria um ambiente de rede muito mais limpo e fácil de gerenciar. Essa redução no volume dos cabos melhora a circulação do ar ao redor dos equipamentos em funcionamento. Um melhor fluxo de ar ajuda a manter as temperaturas operacionais ótimas. Ele prolonga a vida útil dos dispositivos de rede. O cabeamento organizado também facilita a identificação e o acesso para tarefas de manutenção. Isso minimiza os tempos de inatividade e os custos operacionais.
Escalabilidade e Adaptabilidade para o Crescimento Futuro das Redes
As redes dos campi universitários devem evoluir constantemente. Eles precisam dar suporte a novas tecnologias e às crescentes demandas por dados. As soluções em modo único da MPO oferecem escalabilidade e adaptabilidade inerentes. Isso protege os investimentos de infraestrutura de longo prazo do campus.
Design modular para facilitar atualizações e expansões
Os sistemas de cablagem de fibra ótica MPO são projetados para arquiteturas de rede dinâmicas e em crescimentoEles permitem a expansão ao integrar mais fibras, sem a necessidade de grandes alterações na infraestrutura. As organizações podem ajustar facilmente a capacidade da sua rede à medida que a demanda por dados aumenta. Eles utilizam conectores e adaptadores MPO adicionais, com diferentes números de fibras. A natureza modular desses sistemas também permite alterações rápidas no layout da rede. Isso facilita a rápida incorporação de novas tecnologias e equipamentos. Essa flexibilidade é essencial para campi universitários com cargas de trabalho variáveis. Também beneficia aqueles que precisam de uma escalabilidade rápida devido a novos programas acadêmicos ou iniciativas de pesquisa. Ele oferece uma solução de rede preparada para o futuro. Cabos MPO/MTP pré-terminados simplificam significativamente a atualização e a expansão de redes. Um único conector MTP/MPO pode substituir vários conectores LC/SC. Isso leva a uma redução significativa no espaço necessário para o armazenamento. O seu design de tipo “conecte e use” permite uma instalação rápida. Reduz drasticamente o tempo necessário para a implementação. Por exemplo, Uma estrutura de backbone com 144 fibras pode ser implementada em minutos, em vez de horas.
Proteção dos Investimentos de Longo Prazo para a Infraestrutura dos Campi Universitários
Investir em infraestrutura de modo único MPO oferece uma proteção robusta e de longo prazo para as redes dos campi universitários. A alta capacidade de largura de banda e o design modular garantem que a rede seja capaz de atender às demandas futuras. Os campi universitários evitam a necessidade de projetos dispendiosos e disruptivos de reforma da infraestrutura de cabos a cada poucos anos. Cabos MPO/MTP com terminação pré-definida reduzem o espaço necessário em racks. O seu design de tipo “conecte e use” permite uma instalação rápida. Os cabos tronco MPO consolidam múltiplas ligações de fibra para um tamanho físico mínimo. Isso simplifica as conexões de rede. Facilita a rápida construção de infraestrutura essencial. Isso é essencial para gerenciar ambientes de alta densidade e apoiar os futuros avanços tecnológicos. Sistemas de cabos de fibra ótica com terminação pré-definida são amplamente instalados em data centers empresariais, instalações de colocalização, parques de servidores e salas de telecomunicações. Eles funcionam como redes estruturais fundamentais. Eles conectam as portas LC às portas MPO na parte traseira dos painéis de distribuição. Isso facilita diretamente a atualização de conexões de 10 G para velocidades mais altas, como 40/100 G. Por isso, elas são ideais para a evolução da infraestrutura em campi universitários. Esta abordagem inovadora protege o investimento financeiro do campus. Isso garante uma rede confiável e de alto desempenho durante décadas.
Projetar e implementar redes campus de longo alcance com tecnologia MPO
Projetar e implementar uma rede robusta para um campus moderno requer um planejamento e execução cuidadosos. Esse processo garante que a infraestrutura atenda às demandas atuais e apoie o crescimento futuro.
Planejamento e Avaliação Estratégica
O efetivo desenvolvimento de uma rede começa com um planejamento estratégico minucioso. Esta fase envolve a compreensão das necessidades únicas do campus e a antecipação de futuras mudanças tecnológicas.
Avaliação das Atuais e Futuras Necessidades de Largura de Banda
Os planejadores de rede devem primeiro avaliar o consumo atual de largura de banda no campus. Eles analisam dados de vários departamentos, programas acadêmicos e iniciativas de pesquisa. Esta avaliação ajuda a identificar os horários de maior uso e as aplicações críticas. Ao mesmo tempo, eles projetam as necessidades futuras de largura de banda. Esta projeção leva em conta o número previsto de matrículas de alunos, novos projetos de pesquisa e tecnologias emergentes, como a realidade virtual ou a análise avançada de dados. Um entendimento claro desses requisitos orienta a seleção das tecnologias e capacidades de rede adequadas.
Mapeamento do Layout do Campus e Considerações Relativas às Distâncias
É essencial compreender em detalhes o layout físico do campus. Isso inclui a localização de todos os edifícios, suas estruturas internas e as distâncias entre eles.
- Densidade e Distribuição de Usuários: Os projetistas de redes levam em conta onde os usuários se concentram no campus. Isso garante que a capacidade da rede atenda à demanda em todas as áreas.
- Tipos de Cabos (Fibra Ótica vs. Ethernet): A escolha do cabo depende das necessidades de largura de banda, da distância e do custo. Os cabos de fibra ótica permitem percorrer distâncias maiores sem que haja degradação no sinal. Os cabos Ethernet são adequados para distâncias mais curtas ou redes menores.
Um levantamento detalhado no local ou de forma virtual É crucial. Este levantamento mapeia o espaço físico. Identifica desafios estruturais ou ambientais. Ele também determina as necessidades de conectividade, avaliando a densidade de usuários, os tipos de dispositivos e possíveis interferências no Wi-Fi. Dispersão geográfica dos switches de acesso à LAN A necessidade de conexões entre vários edifícios dentro de um complexo maior requer um número maior de interconexões de fibra ótica que levem a um único núcleo central de comunicação. Isso afeta diretamente as considerações relativas ao layout e às distâncias no desenho da rede.
Elaboração de orçamentos e análise do custo total de propriedade
Uma análise abrangente do TCO é essencial para qualquer projeto de rede em larga escala. Esta análise vai além dos preços iniciais de compra. Considera todos os custos associados à rede durante todo o seu ciclo de vida.
Os componentes-chave de uma análise TCO incluem::
- Custos iniciais de aquisição
- Mão de obra de instalação
- Taxas de substituição
- Intervenções de manutenção
- Custos decorrentes de interrupções no funcionamento
A diferença de preço entre os transceptores ópticos é um fator determinante. Os transceptores de fibra monomodal (SMF) são significativamente mais caros do que os transceptores de fibra multimodal (MMF). Essa diferença é especialmente notável em taxas de transferência de dados mais elevadas, por exemplo 8 vezes para 40G e 5 vezes para 100GAs considerações relativas aos custos auxiliares também desempenham um papel importante. O SMF requer um corte e um alinhamento de alta precisão. Isso geralmente requer componentes fabricados com terminações pré-definidas pela fábrica, o que pode aumentar os custos iniciais de implementação. O MMF, com seu núcleo maior, simplifica o processo de terminação dos cabos no campo, o que resulta em menores custos operacionais. O consumo de energia e o sistema de resfriamento também contribuem para as despesas operacionais. Os diodos laser de onda longa da SMF geralmente requerem mais potência e são mais sensíveis à temperatura. Isso pode levar a despesas operacionais mais elevadas com eletricidade e arrefecimento, em comparação com os VCSELs eficientes em termos energéticos utilizados pelos MMF. Embora o SMF tenha custos iniciais de hardware mais elevados, ele oferece um risco quase nulo de necessidade de troca de cabos para futuras aumentações na velocidade. A própria infraestrutura de cabos é, por natureza, preparada para o futuro. O MMF possui custos iniciais de hardware mais baixos, mas apresenta um risco maior de necessidade de reformatação do cabeamento à medida que as velocidades aumentam.
Seleção de Componentes para um Desempenho Robusto
A seleção dos componentes corretos é fundamental para a construção de uma rede de campus MPO de longo alcance confiável e de alto desempenho. Cada elemento desempenha um papel vital na eficiência e na durabilidade do sistema como um todo.
Tipos de Cabos MPO, Número de Fibras e Especificações OS2
Os cabos MPO são conectores com mais de duas fibras. Geralmente, estão disponíveis com 8, 12 ou 24 fibras. Para arranjos de múltiplas fibras de super alta densidade, o número de fibras pode variar de 32 até 144. Vários tipos de cabos MPO são utilizados para fins diferentes:
- Cabos de porta -malas: Esses cabos possuem tipos e números idênticos de conectores em ambas as extremidades. Eles eliminam a necessidade de conversões ou cabos separados. Cabos de tronco São ideais para aplicações de alta densidade e alta velocidade, com perda mínima de sinal.
- Cabos de breakout: Esses cabos combinam ou dividem o fluxo de dados. Por exemplo, eles dividem um único sinal em várias partes (por exemplo, quatro ou oito). Isso simplifica a topologia dos data centers e reduz a necessidade de equipamentos.
- Cabos de Conversão: Semelhantes aos cabos de desconexão, estes disponibilizam diferentes números e tipos de fibras. Por exemplo, um cabo com 24 fibras pode ser convertido em um cabo com 2×12 ou 3×8 fibras. Isso aumenta a flexibilidade do sistema de cablagem, eliminando a necessidade de cabos separados para cada conexão.
Os cabos MPO oferecem fibra OS2 de modo único. Os cabos OS2 são ideais para transmissões de longa distância, suportando distâncias de até 200 km. Isso os torna adequados para instalações em campi universitários, onde a máxima distância e a alta largura de banda são critérios essenciais. A fibra de modo único, como a OS2, possui as seguintes características: Núcleo menor (tipicamente de 8 a 10 micrômetros)Ela transmite a luz diretamente. Este design permite maior largura de banda e distâncias mais longas, geralmente excedendo os 10 km. É particularmente adequado para telecomunicações de longo alcance, redes metropolitanas e infraestruturas de rede em campi universitários, onde a máxima distância e a alta largura de banda são essenciais.
Cassetes MPO, Painéis Adaptadores e Painéis de Conexão
Para um desempenho robusto nas redes de backbone dos campi universitários, recomenda-se o uso de caixas MPO e painéis adaptadores (especificamente módulos LGX com adaptadores MPO integrados). Os adaptadores MPO oferecem baixa perda de inserçãomédia de 0,35 dBApresentam também uma alta perda de retorno (>= 60 dB para conectores polidos do tipo APC). Atendem aos padrões IEC 61754-7 para ambientes de alta confiabilidade. A integração do MPO com módulos LGX proporciona escalabilidade, permitindo adições sem interrupções na rede. Ele garante uma dimensão compacta, alta densidade de portas e desempenho excepcional para comunicações ópticas exigentes. As caixas MPO compatíveis com o padrão LGX são projetadas para serem montadas em painéis de conexão ou gabinetes de fibra ótica do tipo LGX. Isso facilita a instalação e a integração com a infraestrutura existente.
Estes componentes oferecem vários benefícios:
- Organização Melhorada: Eles centralizam os cabos, reduzindo o desordenamento e os erros durante a manutenção.
- Manutenção simplificada: Eles permitem um acesso fácil e a resolução de problemas, reduzindo assim os tempos de inatividade.
- Escalabilidade: Eles facilitam a expansão da rede, permitindo a adição e a reconfiguração fáceis das conexões.
- Integridade de Sinal Melhorada: O correto gerenciamento dos cabos minimiza a flexão e a tensão, preservando o desempenho do sinal.
- Pegada reduzida: Eles são compatíveis com caixas MPO ou módulos LGX, o que permite economizar espaço e alcançar uma alta densidade de portas.
- Cost Efficiency: Eles reduzem a necessidade de reparos/substituições e prolongam a vida útil do cabo.
- Conformidade e Padronização: Eles ajudam a cumprir as regulamentações do setor, graças à sua estrutura uniforme.
Embora os cabos MPO multimodo OM3 ou OM4 sejam adequados para ambientes universitários com distâncias intermediárias e requisitos de largura de banda típicos de grandes empresas, o cabo MPO monomodo OS2 continua sendo a melhor opção para interconexões de longo alcance em ambientes universitários.
Transceptores Compatíveis (ex.: QSFP-DD, OSFP)
A seleção de transceptores compatíveis é de fundamental importância para alcançar as taxas de dados desejadas. Os transceptores convertem sinais elétricos em sinais ópticos e vice-versa. Para as redes de backbone de alta velocidade em campi universitários, transceptores como o QSFP-DD (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable Double Density) e o OSFP (Octal Small Form-factor Pluggable) são bastante comuns. Esses módulos suportam Ethernet de 100G, 400G e até mesmo 800G. Eles devem corresponder ao tipo de fibra (monomodo) e às especificações de comprimento de onda do cabeamento MPO. A seleção adequada do transceptor garante a integridade ótima do sinal e a maior distância de transmissão possível.
Melhores Práticas de Instalação para uma Confiabilidade Ótima
Mesmo com os melhores componentes, práticas de instalação inadequadas podem comprometer o desempenho da rede. A adesão às melhores práticas garante uma confiabilidade e durabilidade ótimas para a instalação de fibra ótica.
Encaminhamento adequado dos cabos, proteção deles e gestão eficaz do raio de curvatura
O manuseio cuidadoso dos cabos de fibra ótica durante a instalação é de extrema importância. O encaminhamento correto dos cabos evita danos e garante um fluxo de ar eficiente. As medidas de proteção protegem os cabos contra esforços físicos e fatores ambientais. Mantecer o raio de curvatura correto é especialmente importante. Exceder o raio mínimo de curvatura pode causar microcurvaturas, o que leva à perda de sinal e a possíveis danos na fibra.
| Prática/Solução | Propósito/Vantagem |
|---|---|
| Gestão Geral de Cabos | Preserva a integridade do sinal, facilita a manutenção, suporta a escalabilidade e reduz o desgaste, minimizando a tensão, as deformações e a exposição ao ambiente. |
| Botinha Mini | Reduz a quantidade de cabos necessários, maximiza o espaço em ambientes de alta densidade, melhora a circulação do ar e suporta configurações de alta densidade. |
| Uniboot | Consolida duas fibras em um único cabo, reduz o volume dos cabos, simplifica as conexões em aplicações duplex, oferece polaridade reversível e melhora a circulação do ar. |
| Bota com Ângulo Flexível | Mantém um raio de curvatura adequado, reduz a perda de sinal causada por curvas excessivas, permite o ajuste em vários ângulos e melhora o controle sobre a posição do cabo. |
| Adaptadores Angulares | Reduz a congestão dos cabos, mantém um roteamento eficiente, permite que os cabos saiam em ângulos ótimos, diminui a tensão e evita dobras excessivas. |
Procedimentos Abrangentes de Teste e Certificação
Após a instalação, testes abrangentes e a certificação são obrigatórios e inegociáveis. Estes procedimentos verificam a integridade e o desempenho das ligações de fibra ótica.
- Métodos de Teste e Limpeza de Conectores MTP/MPO: Os conectores MPO são sensíveis à poeira e a outros contaminantes. Estes causam aproximadamente… 801 falhas de rede do tipo TP3TIsso envolve a inspeção com um microscópio de alta qualidade. Em seguida, é realizada a limpeza com ferramentas secas (limpador de caixas, limpador de canetas MTP/MPO). A limpeza úmida é utilizada quando necessário. Inspeções e limpezas são necessárias toda vez que um cabo MTP/MPO for conectado.
- Verificação do Tipo de Polaridade MTP/MPO: Isso é essencial para garantir a transmissão correta do sinal do transmissor (TX) para o receptor (RX). Uma polaridade incorreta faz com que o sinal seja transmitido na direção errada. Isso afeta o desempenho da rede e pode causar a substituição desnecessária de equipamentos, além de atrasos.
- Teste de Continuidade de Fibra MTP/MPO: Isso confirma a integridade da ligação e a ausência de quebras nas fibras. Ele garante uma transmissão suave do sinal óptico. O localizador de falhas visuais (VFL) identifica e localiza falhas como curvas, quebras e problemas de conexão.
- Fonte de luz MTP/MPO e medidor de potência ótica: Eles quantificam a perda de inserção e garantem que haja um orçamento adequado de potência óptica. A fonte de luz estimula a fibra. O medidor de potência ótica mede a potência do sinal. A seleção de um medidor de potência ótica deve levar em conta as necessidades atuais e futuras em relação ao número de canais e à distância entre eles.
- Teste de OTDR: Isso detecta, localiza e mede eventos em uma ligação de fibra ótica. Simplifica o teste de cabos MTP/MPO. Calcula a atenuação da fibra, a sua uniformidade, bem como as perdas nas junções/conectores. Fornece um registro gráfico das características do sinal.
Estas proceduras são guiadas por padrões da indústria estabelecidos por organizações como a IEC (Comissão Eletrotécnica Internacional) em relação à geometria da fibra, à atenuação e às perdas causadas pela flexão maciça, e pela TIA/EIA (Associação da Indústria de Telecomunicações e Aliança da Indústria Eletrônica) no que diz respeito aos requisitos de certificação para a instalação, como o comprimento da fibra, a polaridade e as perdas no link.
A limpeza é uma questão de extrema importância para as instalações de fibra ótica MPO. Isso é especialmente verdadeiro no caso dos conectores multifibros utilizados em aplicações ópticas paralelas de alta velocidade (por exemplo,...) 100, 200, 400 e 800 GbEOs contaminantes podem migrar facilmente entre as fibras dentro de um arranjo desse tipo. As variações de altura entre as fibras podem dificultar uma limpeza adequada. Para garantir consistência e objetividade na inspeção de fibras, a norma IEC 61300-3-35 define critérios para a conformidade dos microscópios, procedimentos de inspeção e classificações específicas de limpeza para a emissão de certificados de aprovação/reprovação. Este padrão classifica os defeitos em arranhões (características lineares permanentes) e outros tipos de defeitos (características não lineares). Ele divide a superfície terminal da fibra em quatro zonas: Zona A (núcleo), Zona B (revestimento), Zona C (adesivo) e Zona D (contato ou ferrula). A Zona A possui os requisitos mais rigorosos para a aprovação ou rejeição dos produtos, seguida pela Zona B. A contaminação nessas áreas afeta diretamente a transmissão do sinal. Para os conectores MPO, a norma IEC 61300-3-35 recomenda a inspeção de toda a estrutura do conector para remover quaisquer partículas soltas antes de se concentrar nas zonas A e B das superfícies terminais individuais. Isso requer microscópios com um grande campo de visão (pelo menos 6,4 × 2,5 mm), capazes de detectar detritos com diâmetro de 10 µm. Cada face final da fibra deve ser inspecionada e certificada de acordo com a norma IEC 61300-3-35 antes da sua conexão. Isso garante a disponibilidade contínua da rede, o desempenho na transmissão de sinais e a confiabilidade dos equipamentos.
A certificação de nível 1, de acordo com o padrão TIA-568: Cabos e Componentes de Fibra Ótica, é essencial para instalações de fibra ótica do tipo MPO. Envolve a verificação da atenuação dos cabos de fibra ótica instalados, utilizando um conjunto de equipamentos para teste de perdas ópticas (OLTS). Além disso, também verifica o comprimento e a polaridade dos cabos. A medição da perda de inserção é fundamental para confirmar que a ligação atende ao orçamento previsto para as perdas. Um OLTS consiste em um medidor de potência ótica e uma fonte de luz. Eles podem ser integrados ou utilizados em pares. Medições precisas e válidas dependem não apenas do equipamento adequado, mas também da seleção da melhor técnica de referência. O método de referência com um único cabo, recomendado pela TIA e pela IEC, oferece alta precisão no teste de ligações de fibra ótica de ponta a ponta, incluindo as perdas nos conectores. A inspeção dos conectores é igualmente vital. Oitenta por cento dos problemas de rede são atribuídos a conectores sujos. Para os conectores MPO, um único conector sujo ou danificado pode afetar até 24 fibras. Isso leva a interrupções significativas no serviço. A inspeção deve ser realizada utilizando um óculo de inspeção de fibra ótica que ofereça imagens em alta definição, bom contraste e um amplo campo de visão, a fim de detectar com precisão quaisquer defeitos. As soluções mais recentes oferecem inspeção automatizada, reduzindo o tempo necessário para menos de 10 segundos. Inspecionar os conectores na fase de instalação é essencial para evitar futuros problemas de rede e garantir um desempenho otimizado. Isso é especialmente verdadeiro para taxas de transmissão elevadas 25, 40, 100 ou 400 Gbit/sque possuem margens de erro mínimas.
Documentação Abrangente da Usina de Fibra
A documentação detalhada de toda a instalação de fibra ótica é uma prática recomendável e essencial, mas que muitas vezes é negligenciada. Isso inclui registros precisos das rotas dos cabos, das atribuições das fibras, dos tipos de conectores e dos resultados dos testes. Uma documentação abrangente simplifica a resolução de problemas, a manutenção e as atualizações futuras. Fornece um roteiro claro para a infraestrutura de rede. Isso garante um gerenciamento eficiente e reduz a possibilidade de interrupções no funcionamento do sistema.
Topologias de Rede Comuns para Backbone de Campi Universitários
O projeto da estrutura de rede principal de um campus requer uma análise cuidadosa da topologia. A estrutura escolhida afeta a confiabilidade, a escalabilidade e o desempenho da rede. Os campi universitários costumam utilizar diversas topologias para garantir uma conectividade robusta e eficiente entre os edifícios.
Implementação de Topologias Estrela e Malha para Redundância
Os projetistas de redes costumam implementar topologias em estrela e em malha para alcançar a redundância nos backbones dos campus. Cada topologia oferece vantagens e considerações distintas para ambientes de campus.
Uma rede estelar utiliza um nó central. Este design faz com que seja possível… vulnerável a um único ponto de falhaSe o nó central falhar, toda a rede perde a conectividade. Essa suscetibilidade destaca uma limitação fundamental das configurações estelares para as estruturas de backbone críticas em campi universitários.
Em contraste, as redes de malha oferecem confiabilidade e redundância superiores. A topologia de malha cria múltiplas rotas entre os dispositivos. Este design oferece o mais alto nível de tolerância a falhas. As configurações incluem a rede em malha completa, na qual cada dispositivo se conecta a todos os outros, e a rede em malha parcial, que utiliza conexões redundantes seletivas. As redes mesh distribuem o encaminhamento de dados entre vários nós. Isso permite o redirecionamento automático de dados por caminhos alternativos caso um nó ou uma ligação falhe. Essa capacidade garante a disponibilidade contínua do sistema e a sua integridade.
As topologias de malha oferecem várias vantagens:
- Máxima tolerância a falhas e redundância.
- Vários caminhos de dados evitam o surgimento de gargalos.
- Excelente para aplicações de missão crítica.
- Capacidades de autoliquidação.
Isto estrutura de rede altamente interconectada Reduz a dependência de um único ponto de falha. Melhora a segurança e a eficiência. As redes mesh também oferecem velocidades de transmissão de dados mais elevadas e maior escalabilidade. No entanto, eles vêm acompanhados por uma maior complexidade e custo. As considerações relativas à implementação incluem o custo mais elevado, a gestão complexa e a necessidade de um extenso sistema de cabos. As topologias de malha são mais adequadas para infraestruturas críticas. Exemplos incluem sistemas de negociação financeira e serviços de emergência. São amplamente utilizados em infraestruturas críticas e redes sem fio que exigem alta confiabilidade.
Para redes empresariais e de campus Recomendam-se configurações híbridas ou em redeUma topologia híbrida combina elementos de diferentes estruturas, como a estrela e a malha. Esta abordagem atende a necessidades específicas, equilibrando a escalabilidade com a confiabilidade. Permite uma arquitetura de rede personalizável e eficiente, baseada em casos de uso específicos. No entanto, os designs híbridos podem aumentar os custos com cabos e manutenção. As topologias em malha fornecem múltiplos caminhos de dados, melhorando significativamente a confiabilidade da rede. Eles permitem o redirecionamento de dados caso um nó ou uma ligação falhe. As topologias em barramento ou em estrela são mais vulneráveis a pontos únicos de falha. Uma topologia bem projetada é essencial para reduzir os períodos de inatividade do sistema.
Considerações sobre Topologias em Anel em Cenários Específicos
As topologias em anel também desempenham um papel no projeto de redes corporativas, especialmente em cenários específicos. Em uma topologia de anel básica, cada dispositivo se conecta a exatamente dois outros dispositivos, formando um caminho circular. Os dados viajam ao redor do anel em uma única direção ou em ambas as direções.
A topologia em anel pode oferecer redundância se for projetada com caminhos duplos, como anéis que giram em sentidos opostos. Se um link falhar, os dados podem ser transmitidos na direção oposta ao longo do anel. Isso mantém a conectividade. Este design é mais fácil de cablar do que uma estrutura em malha completa e pode ser mais econômico para certos layouts de campus. Por exemplo, um anel pode conectar uma série de edifícios localizados ao longo de um caminho linear.
No entanto, as topologias em anel têm suas limitações. Uma única falha pode perturbar todo o sistema se o mecanismo de redundância falhar ou não for completamente implementado. A escalabilidade também pode ser um problema. Adicionar novos dispositivos requer quebrar o ciclo existente para inserir a nova conexão. Isso pode causar interrupções temporárias na rede. Portanto, os campi universitários normalmente utilizam topologias em anel para segmentos específicos ou como sub-redes dentro de uma estrutura principal maior e mais robusta. Eles são menos comuns quando utilizados como estrutura principal para um campus grande e complexo, em comparação com designs de tipo mesh ou híbridos. Uma solução robusta de MPO para longas distâncias integra frequentemente essas topologias para criar uma rede resiliente e de alto desempenho.
Enfrentando Desafios e Assegurando o Sucesso a Longo Prazo com as Soluções MPO de Longo Alcance
Relação Custo-Eficácia: Investimento Inicial versus Economias de Longo Prazo
O investimento inicial em soluções MPO/MTP, incluindo as opções de modo único, pode ser maior do que o necessário para conexões tradicionais. No entanto, essas soluções oferecem economias significativas de custos a longo prazo. O trabalho de instalação reduzido, o menor número de componentes necessários e a simplificação da gestão da infraestrutura contribuem para essas economias. O design modular também permite uma expansão da rede de forma contínua, sem a necessidade de grandes reformas na infraestrutura. Isso aumenta ainda mais o valor a longo prazo.
Para fibras OS2 de modo único em soluções MTP/MPO, os custos com materiais podem ser inicialmente mais elevados. No entanto, elas oferecem um maior valor a longo prazo para aplicações que necessitam de distâncias maiores ou da possibilidade de expansão da largura de banda no futuro. A diferença de preço entre transceptores de modo único e de modo múltiplo está diminuindo. Isso torna as configurações do OS2 mais atraentes para novas instalações. A arquitetura “plug-and-play” das soluções MTP MPO facilita uma instalação mais fácil e rápida. Isso reduz os custos de mão de obra para ambos os tipos de fibra. As implementações do OS2 também são conhecidas por sua durabilidade e desempenho estável. Isso resulta em custos de manutenção a longo prazo mais baixos em comparação com as opções OM3/OM4. Estes podem ter taxas de substituição mais elevadas ao longo de períodos prolongados.
O cálculo do custo total de propriedade mostrou que o maior custo unitário da MTP era compensado por uma menor taxa de falhas e por uma maior eficiência na manutenção. Isso resultou em despesas operacionais 23% menores em comparação com implementações anteriores baseadas no MPO. Em ambientes de hiperescala, a arquitetura baseada em MTP reduziu a área ocupada pelos painéis de fibra em 67% em comparação com designs duplos de LC equivalentes. Isso liberou unidades de rack. Esta eficiência no uso do espaço, cujo valor é de $250 por unidade de rack por ano, permitiu financiar o custo adicional do serviço MTP em apenas nove meses, em uma instalação de colocalização localizada em Manhattan.
Análise dos Reduzidos Custos Operacionais e de Manutenção
| Cable Type | Faixa de custo inicial | Considerações de longo prazo |
|---|---|---|
| Cabos de tronco MTP/MPO | $200 – $500 | Custo inicial mais alto, mas custos de manutenção menores devido à menor quantidade de conexões e ao reduzido risco de erros na instalação. Uma maior capacidade de largura de banda permite futuras atualizações. |
Comparação com Soluções Tradicionais ao Longo do Ciclo de Vida
A tabela acima destaca os benefícios a longo prazo do MTP/Cabos de tronco MPOEmbora seu custo inicial possa ser mais alto, eles resultam em despesas de manutenção menores. Isso se deve ao menor número de terminações e à redução do risco de erros na instalação. A sua maior capacidade de largura de banda também permite futuras atualizações. Isso garante que a rede se mantenha relevante ao longo dos anos.
Estratégias de Manutenção e Resolução de Problemas
Uma manutenção adequada e estratégias eficazes de resolução de problemas são essenciais para a longevidade da rede, especialmente no caso das redes campus de longa distância tipo MPO.
Melhores Práticas para Testes e Diagnóstico de Fibra Ótica
- Limpeza: Realize até três tentativas de limpeza antes de substituir um conector ou cabo. Sempre verifique ambos os conectores de acoplamento. Se a limpeza a seco não funcionar, use um método híbrido com solvente. Assegure-se de que o conector esteja completamente seco antes de conectá-lo. Sempre reinspecione após a limpeza.
- Teste de Polaridade: Assegure-se de que a polaridade esteja correta. Isso confirma que os sinais seguem o caminho correto. Verifica também se as conexões entre os dispositivos transmissor e receptor estão intactas. Isso evita problemas como sinais sendo enviados na direção errada.
- Teste de Continuidade: Utilize uma fonte de luz ou um localizador de falhas visuais. Isso confirma que não existem interrupções no link. Isso garante que a luz chegue corretamente até o seu destino final. Este rápido teste de validação durante a instalação previne problemas futuros.
- Certificação de Nível 1: De acordo com a TIA-568, isso envolve o teste de atenuação utilizando um conjunto de teste de perdas ópticas (OLTS). Além disso, também é verificado o comprimento do cabo e sua polaridade. A medição da perda de inserção é essencial para que seja possível cumprir o orçamento previsto para as perdas. Um OLTS inclui um medidor de potência ótica e uma fonte de luz.
- Inspeção do Conector: Utilize um óculo de inspeção com lentes maiores e LEDs na faixa do violeta (405 nm). Isso proporciona uma maior clareza na visualização. Detecta pequenos defeitos, mesmo aqueles com apenas 2 µm de tamanho. Inspecione os conectores durante a instalação. Isso ajuda a encontrar imperfeições, limpar as áreas sujas ou substituir as peças danificadas antes da implementação. O método “inspecionar, limpar, reinspecionar” garante a limpeza.
Os loops de fibra são ferramentas essenciais para o teste de redes ópticas. Eles direcionam os sinais transmitidos de volta para o receptor. Isso testa a funcionalidade dos transceptores ópticos e dos portos. Os loopbacks MPO são especialmente úteis para interfaces de alta densidade e alta velocidade, como as Ethernet de 400G e 800G. São cruciais para a ótica paralela em redes de 40G, 100G, 400G e 800G. A limpeza regular das superfícies dos conectores de tipo loopback de fibra ótica e o armazenamento adequado são orientações importantes para a manutenção desses dispositivos.
Monitoramento Proativo e Medidas Preventivas
Implemente sistemas de monitoramento contínuo. Esses sistemas monitoram o desempenho da rede. Eles identificam potenciais problemas de forma precoce. Inspeções regulares da infraestrutura física também ajudam a prevenir problemas. Esta abordagem proativa minimiza os períodos de inatividade e garante o funcionamento consistente da rede.
Assegurar a limpeza e o manuseio corretos dos conectores MPO
A Importância Crítica da Limpeza dos Conectores
Os conectores MPO são sensíveis à poeira e a outros contaminantes. Elas são responsáveis por uma grande percentagem de falhas na rede. Os contaminantes podem se mover facilmente entre as fibras dentro de um arranjo desse tipo. Isso torna a limpeza de extrema importância para um desempenho confiável.
Ferramentas e Procedimentos de Limpeza Recomendados
Utilize ferramentas de limpeza a seco, como limpadores de caixas ou limpadores de canetas do tipo MTP/MPO. Se necessário, utilize um método híbrido com solvente. Assegure-se sempre de que o conector esteja completamente seco antes de conectá-lo. Inspeccione cada face final da fibra antes da conexão. Isso evita a degradação do sinal e garante a saúde ótima da rede.
Escalabilidade para futuras atualizações e avanços tecnológicos
Os campi universitários necessitam de uma infraestrutura de rede capaz de se adaptar à constante evolução tecnológica. As soluções de modo único MPO oferecem escalabilidade e adaptabilidade inerentes. Isso protege os investimentos de infraestrutura de longo prazo do campus.
Planejamento para maiores quantidades de fibras e maior modularidade
As conexões MPO oferecem uma excelente escalabilidadeEles permitem o crescimento futuro da rede sem a necessidade de reformas extensivas no cabeamento ou alterações significativas na infraestrutura. Isso os torna componentes cruciais em data centers contemporâneos e em outras localidades com redes densamente populadas. Eles atendem tanto às necessidades imediatas de desempenho quanto às possibilidades de expansão futura. A tecnologia MPO é conhecida por sua excelente escalabilidade. Os fornecedores de serviços podem expandir facilmente os pontos de conexão sem necessidade de uma reforma completa. Esta solução resiliente mantém a confiabilidade da rede. Atende às atuais demandas de comunicação, bem como aos avanços tecnológicos previstos no futuro.
Conjuntos de cabos MPO de alta densidade Atender à necessidade de aumentar as velocidades de transferência de dados e as larguras de banda nos data centers. Eles utilizam conectores com muitas fibras. Isso reduz o tamanho do cabo e melhora a circulação do ar. Otimiza a utilização do espaço e o sistema de resfriamento. As características principais incluem…:
- Grande número de fibras: Cada conector suporta 12, 24 ou até mesmo 72 fibras.
- Baixo Impacto Ambiental: Ocupa menos espaço, o que facilita a organização dos cabos.
- Instalações Rápidas: Os técnicos as instalam e reconfiguram de forma rápida.
- Escalabilidade: Eles se integram facilmente à infraestrutura existente, ao mesmo tempo em que suportam o crescimento futuro da rede.
Os cabos tronco MPO oferecem excelente escalabilidade e modularidadeIsso é essencial para data centers que precisam expandir sua infraestrutura. Eles ajudam a garantir que a infraestrutura dos data centers seja adequada para as necessidades futuras. Eles permitem um crescimento incremental na capacidade de rede. Eles permitem futuras atualizações sem a necessidade de grandes reformas na fiação, à medida que as demandas por largura de banda aumentam. A expansão da rede torna-se mais simples com cabos MPO devido à conectividade de alta densidade (de 12 a 144 fibras em um único conector). Isso reduz o espaço físico necessário e simplifica os procedimentos de conexão. O mecanismo de acoplamento tipo “empurrar-puxar” dos conectores MPO acelera o processo de encaixe das fibras. Isso facilita a instalação e a expansão. Os comprimentos dos cabos personalizáveis reduzem o excesso de cabos e facilitam o seu gerenciamento. Isso facilita a manutenção e a atualização dos sistemas.
A modularidade dos conectores de fibra ótica MPO permite uma montagem e desmontagem fáceis dos componentes. Os operadores de rede substituem ou atualizam rapidamente os conectores, sem a necessidade de ferramentas especializadas ou de interrupções prolongadas no funcionamento da rede. A capacidade de funcionamento “plug and play” é um elemento fundamental. Permite o funcionamento imediato após a inserção, sem necessidade de configurações complexas. Isso é essencial para uma implementação rápida em data centers. Essa facilidade em adicionar ou remover conexões aumenta a agilidade e a resiliência da rede. A padronização realizada por organizações como a ITU e a TIA garante a compatibilidade e a intercambiabilidade entre diferentes fabricantes. Isso facilita a adoção generalizada e a preparação da infraestrutura para futuras necessidades em aplicações de alta densidade.
Adaptação a Novos Padrões e Aplicações de Ethernet
A adoção de conectores MPO avançados, especialmente as variantes de alta densidade, alinha-se com a tendência da indústria em direção a taxas de transmissão de dados mais elevadas, como 400G e 800G. Essas taxas exigem um maior número de fibras e um uso mais eficiente do espaço. Os conectores MPO, ao suportarem a tecnologia de conexão push-on para múltiplas fibras, permitem que os data centers escalem suas operações sem comprometer o desempenho ou incorrer em custos adicionais significativos para atualizações da infraestrutura.
Tendências futuras na tecnologia de cabos MPO incluir:
- Taxas de transferência de dados mais elevadas: Isso gera a necessidade de soluções MPO de 400G e 800G. Isso requer novos tipos de conectores, como os conectores MPO-16 e MPO-32, a fim de aumentar o número de fibras e a largura de banda disponível.
- Automação e inteligência: Isso resulta em sistemas de cabos MPO mais inteligentes, dotados de funcionalidades de diagnóstico e gerenciamento integradas. Eles oferecem monitoramento em tempo real e resolução automática de problemas.
- Soluções modulares e flexíveis MPO: Os sistemas de caixas modulares MPO permitem uma escalabilidade e reconfiguração mais fáceis. Eles atendem às necessidades dinâmicas dos data centers.
- Fibras insensíveis à flexão: Elas aumentam a flexibilidade física e a resistência. Eles garantem um bom desempenho em ambientes hostis e de alta densidade.
Conectores MPO de alta densidade são essenciais para maximizar a eficiência do uso do espaço e a capacidade de largura de banda em data centers, setores de telecomunicações e ambientes de computação de alto desempenho. Um único Conector MPO-24 Substitui até 24 conectores simplex. Isso aumenta significativamente a densidade de fibras e economiza espaço nos racks. A tendência para densidades portuárias mais elevadas (de 32 a 128 ou mais portas) nos racks de data centers destaca a demanda por esses conectores. A miniaturização dos conectores MPO, assim como as versões compactas dos conectores MTP, otimiza o espaço sem comprometer o desempenho. Eles apresentam baixa perda de inserção (até 0,2 dB) e alta perda de retorno (superior a 60 dB). Os avanços tecnológicos na fabricação de cerâmica de alta precisão e na soldadura a laser permitem a produção desses conectores miniaturizados e de alta densidade com maior precisão e confiabilidade. O aumento previsto no uso de fibras ópticas dentro dos data centers, superior a 301 TP3T até 2025, destaca ainda mais a necessidade de conectores compactos e de alto desempenho.
Cabos de conexão MPO: Melhorando a conectividade no campus
Os cabos de conexão MPO oferecem uma solução versátil para redes universitárias. Eles preenchem a lacuna entre os cabos de tronco MPO de alta densidade e os dispositivos de rede individuais. Isso melhora a conectividade e simplifica a implementação em vários prédios do campus.
Compreender a funcionalidade do cabo de conexão MPO
Os cabos de conexão MPO desempenham um papel crucial na infraestrutura de fibra ótica. Eles permitem uma distribuição eficiente de fibras, desde conexões MPO de alta densidade até equipamentos individuais.
Transição do tronco MPO para conectores individuais (LC, SC, FC)
Cabos de distribuição MPO, também conhecidos como cabos de feixe, cabos de divisão ou cabos de expansãoSão essenciais para distribuir várias fibras a partir de um conector MPO para dispositivos individuais. Eles permitem a redistribuição de várias fibras ópticas para dispositivos individuais, sem a necessidade de equipamentos de rede adicionais. Esses cabos simplificam a transmissão de dados over curta distância, mesmo em ambientes desafiadores.
Os conjuntos de cabos MPO utilizam cabos de alta densidade e conectores MPO/MTP. Eles utilizam um kit de adaptação para fazer a transição de um cabo tronco para conectores ópticos genéricos, como… LC, SC, FC, ST ou MTRJEsses cabos possuem um conector MPO/MTP em uma extremidade e conectores de fibra individuais (como LC, SC ou ST) na outra extremidade. O seu uso principal é conectar um único porto MPO a dispositivos individuais que requerem diferentes tipos de conectores, como LC ou SC. Essa funcionalidade é particularmente comum em… centros de dados para conexões de servidores ou switchesIsso facilita a transição de conexões MPO de alta densidade para terminações de fibra única.
Solução de Conexão de Fibra Ótica de Alta Densidade
Os cabos de desconexão MPO oferecem uma solução de conexão de fibra ótica de alta densidade. Eles consolidam muitas fibras em um único cabo, reduzindo o seu volume e facilitando o gerenciamento dos cabos. Este design é essencial para otimizar o espaço em ambientes de rede lotados.
Vantagens na Implantação de Redes no Campus
Os cabos de conexão MPO oferecem várias vantagens para a implementação de redes em campi universitários. Eles simplificam as conexões e aumentam a eficiência.
Facilitando a Conexão com os Equipamentos de Distribuição
Os cabos de desconexão MPO otimizam o espaço físico em data centers, ao consolidar muitas fibras em um único conector, reduzindo significativamente a área necessária para o cabeamento. Por exemplo, uma… O cabo de distribuição MPO com 12 fibras consolida seis transceptores LC duplos Tudo é integrado em um único conector MPO, o que reduz o volume e a bagunça. Isso também melhora a circulação de ar e a eficiência do resfriamento nos racks, o que pode resultar em economias de energia. Esses cabos reduzem os custos de substituição de equipamentos, permitindo que novos switches de alta velocidade se conectem a placas de interface de rede de servidores mais antigas, prolongando assim a vida útil do hardware. Eles também simplificam a gestão de estoques ao padronizar o uso de um número menor de tipos de cabos, reduzindo assim os custos administrativos e os erros.
Reduzir o tempo de instalação e minimizar os erros humanos
A natureza pré-terminada dos cabos MPO reduz significativamente o tempo de instalação. Os técnicos simplesmente conectam-nos, eliminando a necessidade de terminação de fibra no local. Esta abordagem de “conectar e usar” minimiza o potencial de erros humanos durante a implementação.
Principais características e especificações
Os cabos de conexão MPO vêm com características e especificações específicas. Eles garantem um desempenho e segurança otimizados.
Quantidades disponíveis de fibras (12, 24, 48) e tipos de fibras (OS2, OM3/4/5)
Os cabos de conexão tipo MPO são comumente disponíveis com… 8, 12, 16, 24 e até mesmo 48 fibrasEles suportam vários modos de transmissão de fibra:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Contagem de fibra | 8, 12, 24 fibras |
| Modo de Fibra | Modo único: OS2 9/125μm |
| Multimodo: OM3 50/125μm, OM4 50/125μm, OM5 |
Estes cabos são disponíveis em… multimodo (OM3, OM4) Para transmissões de curta distância, utiliza-se o modo único (OS2); para aplicações de longa distância, utiliza-se outro tipo de tecnologia.
Desempenho com baixas perdas e conformidade com os padrões da indústria
Os cabos de conexão MPO/MTP são projetados para atender aos requisitos de perda de inserção “padrão” e “baixa perda”.
| Insertion Loss (dB) | Perda Padrão | Baixa perda | Perda ultrabaixa |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | ≤ 0,5 | ≤0.35 | ≤0.25 |
O conector MPO geralmente apresenta uma perda de inserção de… Máximo de 0,35 dB (Típico de 0,15 dB) E uma perda de retorno de ≥20 dB. Os conectores LC possuem uma perda de inserção de ≤0,2 dB e uma perda de retorno de ≥20 dB.
Jaqueta LSZH para maior durabilidade e segurança
Os conectores de fibra MTP/MPO-LC estão disponíveis com um revestimento de alta qualidade, do tipo LSZH (Baixo Fumo, Sem Halogênios), além de opções como PVC e OFNP. Esse material escolhido para a jaqueta garante a durabilidade, a segurança do cabo e seu cumprimento com requisitos ambientais específicos, especialmente no que diz respeito à segurança contra incêndios. Por razões de segurança, os planejadores de redes devem selecionar revestimentos de cabos com propriedades retardantes à chama, como… LSZH: baixa emissão de fumaça e baixa toxicidadeOu PVC, para resistência ao fogo.
As soluções de modo único MPO oferecem uma infraestrutura robusta, escalável e eficiente para conectar os edifícios do campus. Essas soluções atendem de forma eficaz à necessidade crucial de uma infraestrutura de rede de alta velocidade, confiável e preparada para o futuro. Os campi universitários adotam essa tecnologia. Isso garante que eles estejam bem equipados para atender às demandas atuais e futuras por dados. Também apoia a inovação e o crescimento em toda a instituição.
FAQ
O que é fibra ótica de modo único MPO?
A fibra ótica de modo único MPO combina conectores do tipo “Multi-fiber Push On” com fibra ótica de modo único. Esta solução oferece conectividade de alta densidade. Suporta a transmissão de dados over longas distâncias. Lida de forma eficiente com as altas exigências de largura de banda dos backbones dos campi universitários.
Por que os campi universitários deveriam escolher as soluções de modo único da MPO?
Os campi escolhem o MPO de modo único devido à sua largura de banda inigualável, alcance prolongado e instalação simplificada. Suporta aplicações de alta velocidade, como o Ethernet de 400 Gbps. Esta tecnologia assegura a capacidade da rede de atender às demandas crescentes por dados em edifícios dispersos.
Como as soluções de modo único MPO apoiam o crescimento futuro das redes?
As soluções em modo único da MPO oferecem um design modular e um alto número de fibras. Isso permite atualizações e expansões fáceis. Eles se adaptam facilmente a novos padrões e aplicações de Ethernet. Isso protege os investimentos de infraestrutura de longo prazo do campus.
Que benefícios os cabos MPO pré-terminados oferecem durante a instalação?
Cabos MPO pré-terminados Chega pronto para uso imediato. Eles reduzem significativamente o tempo de instalação e os custos de mão de obra. Esta abordagem do tipo “conecte e use” minimiza a necessidade de procedimentos de emenda no local. Também reduz o potencial de erros humanos durante a implementação.
Como os cabos de conexão MPO melhoram a conectividade dentro dos campi universitários?
Cabos de chicote de fuga MPO Transição de troncos MPO de alta densidade para conectores individuais, como LC ou SC. Eles facilitam a conexão com os equipamentos de distribuição. Esta solução reduz o tempo de instalação e minimiza os erros humanos nas implementações de redes em campi universitários.
O MPO de modo único é uma solução econômica e eficaz para campi universitários?
O modo único MPO envolve um investimento inicial mais elevado. No entanto, proporciona economias significativas a longo prazo. Essas economias resultam da redução dos custos com mão de obra de instalação, de uma manutenção mais barata e da capacidade da rede de se adaptar às necessidades futuras. Isso minimiza a necessidade de projetos dispendiosos de reformulação do cabeamento.
Por que a limpeza dos conectores MPO é importante para a confiabilidade da rede?
Os conectores MPO são altamente sensíveis à poeira e a outros contaminantes. Elas são responsáveis por uma grande percentagem de falhas na rede. Uma limpeza adequada garante a transmissão ótima do sinal. Ele evita a degradação do desempenho e mantém a disponibilidade da rede. 🧼



